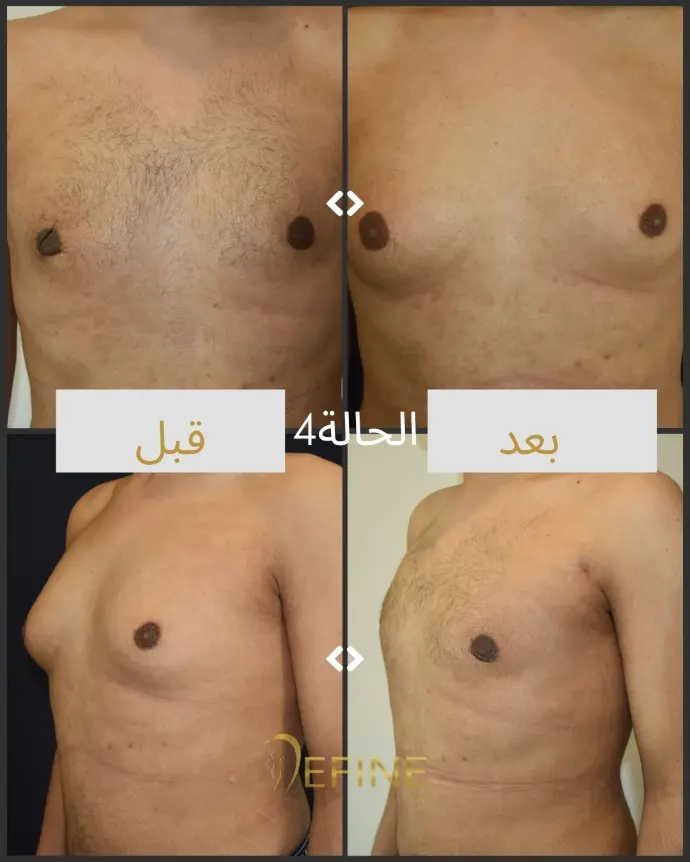
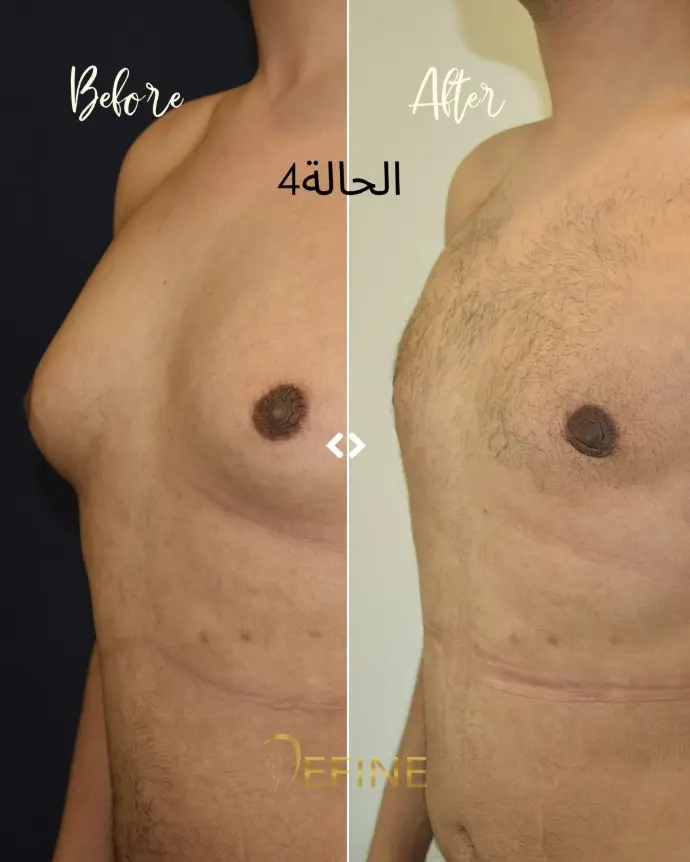
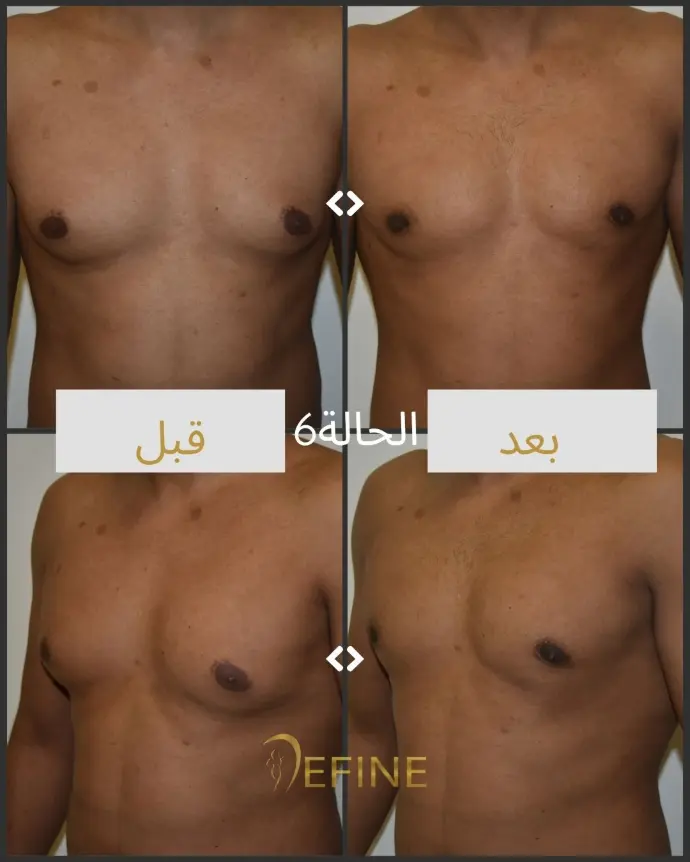
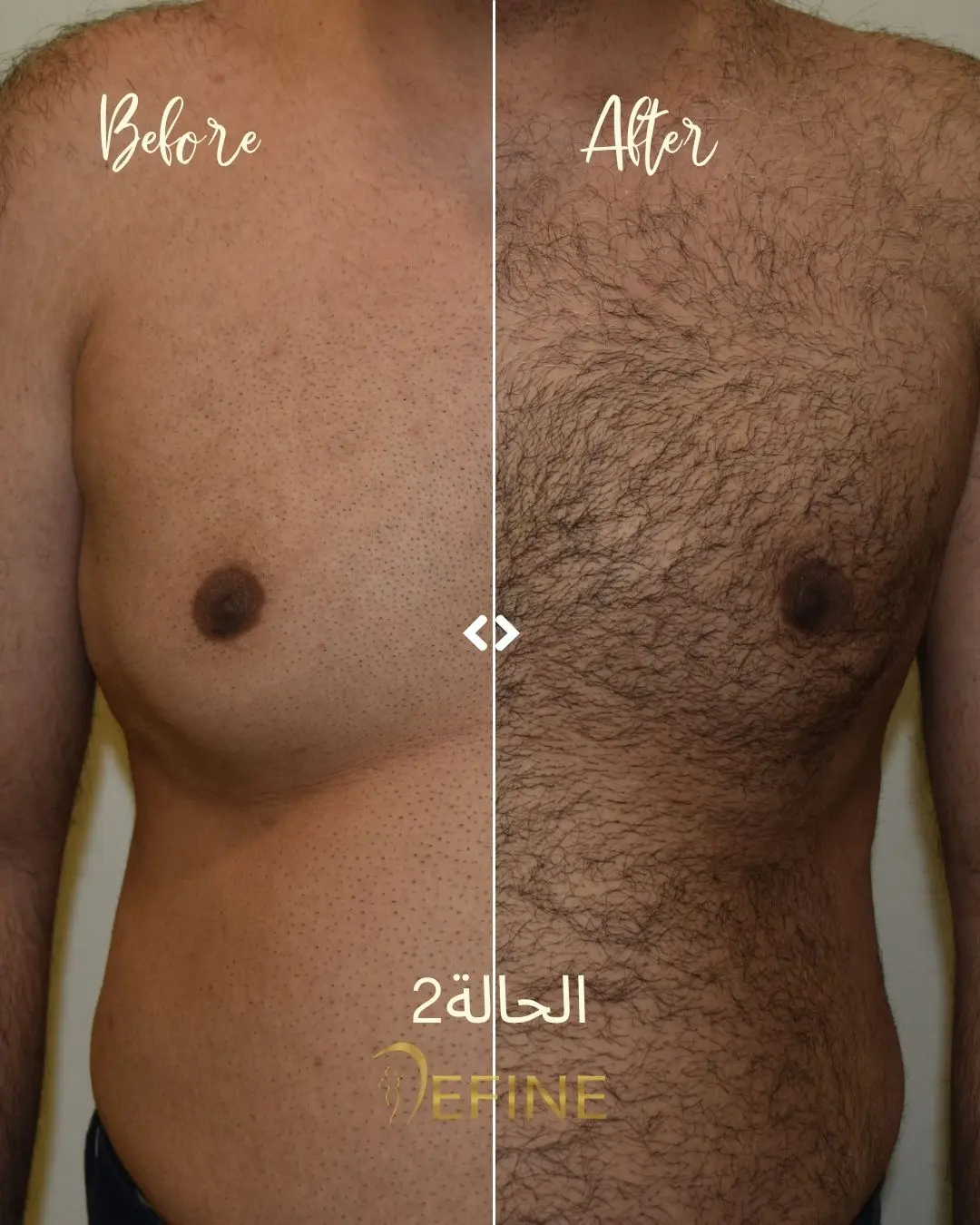
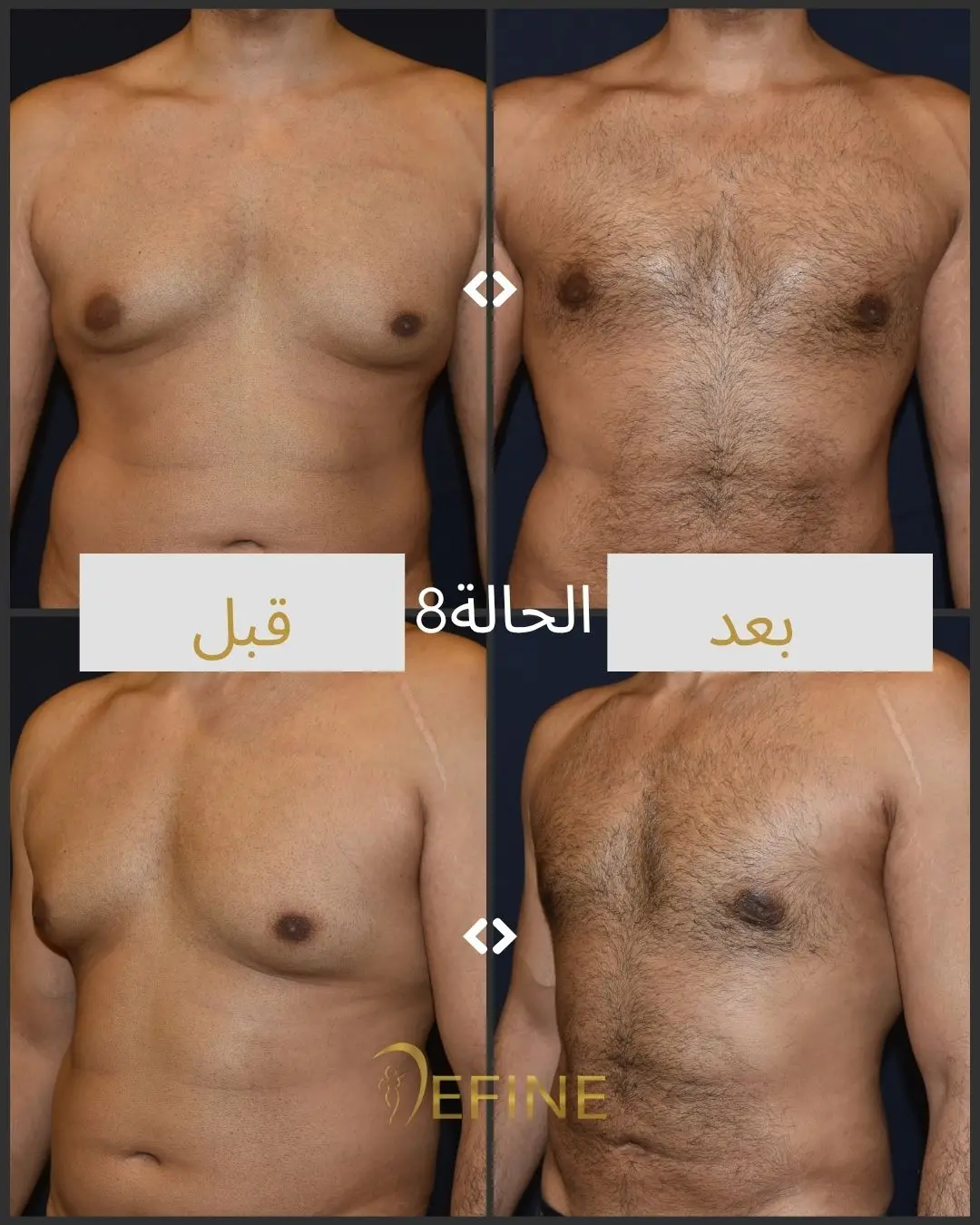
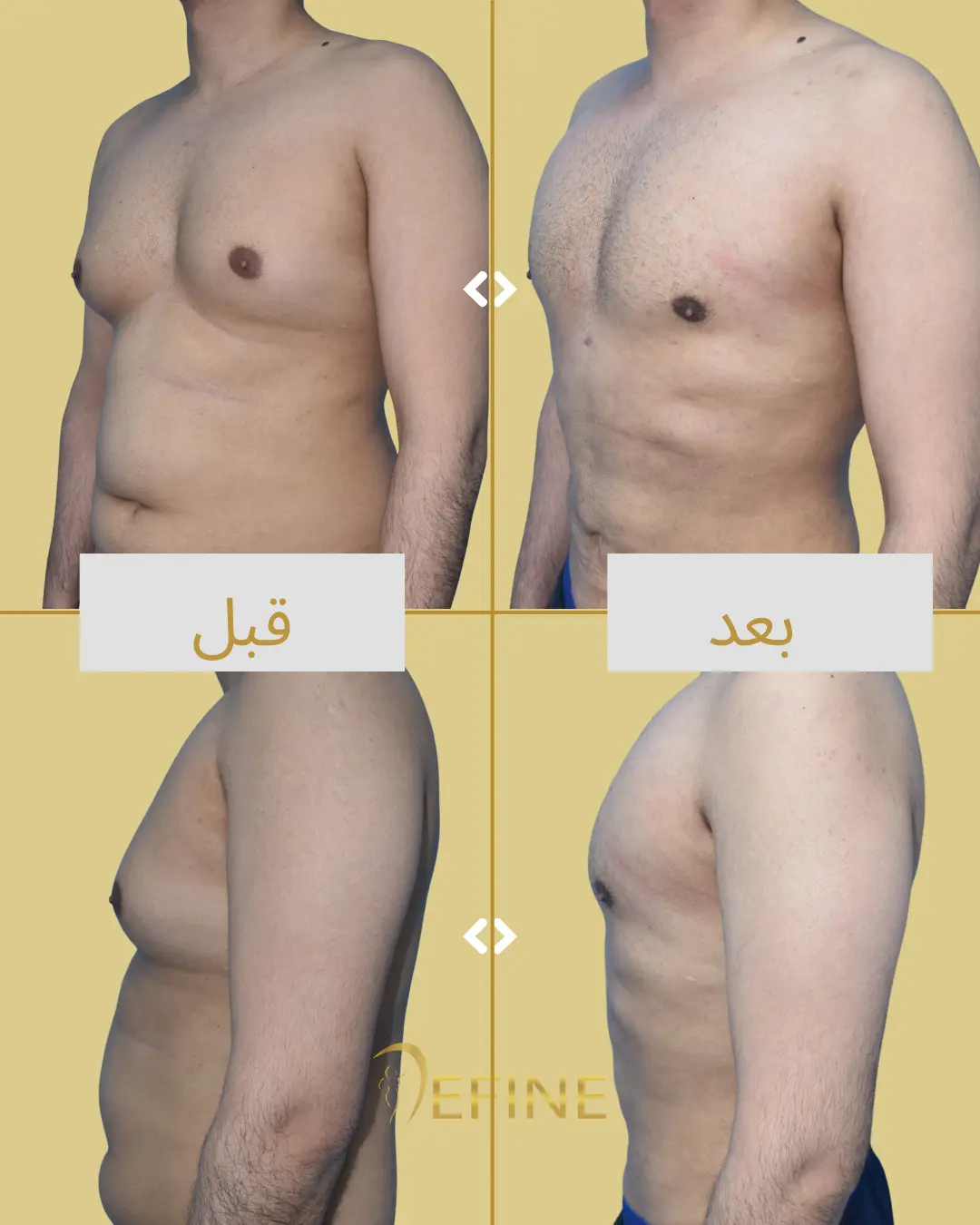
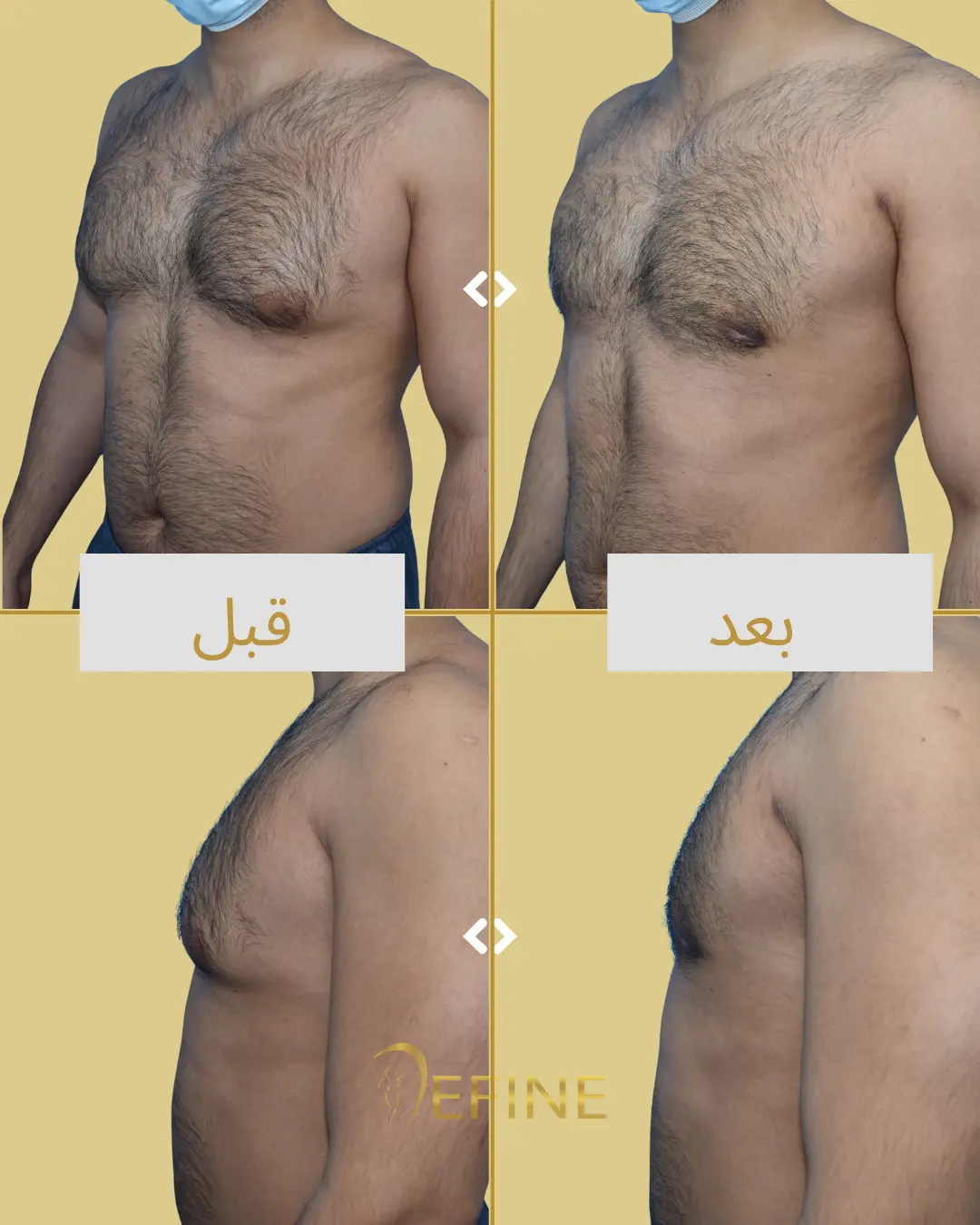
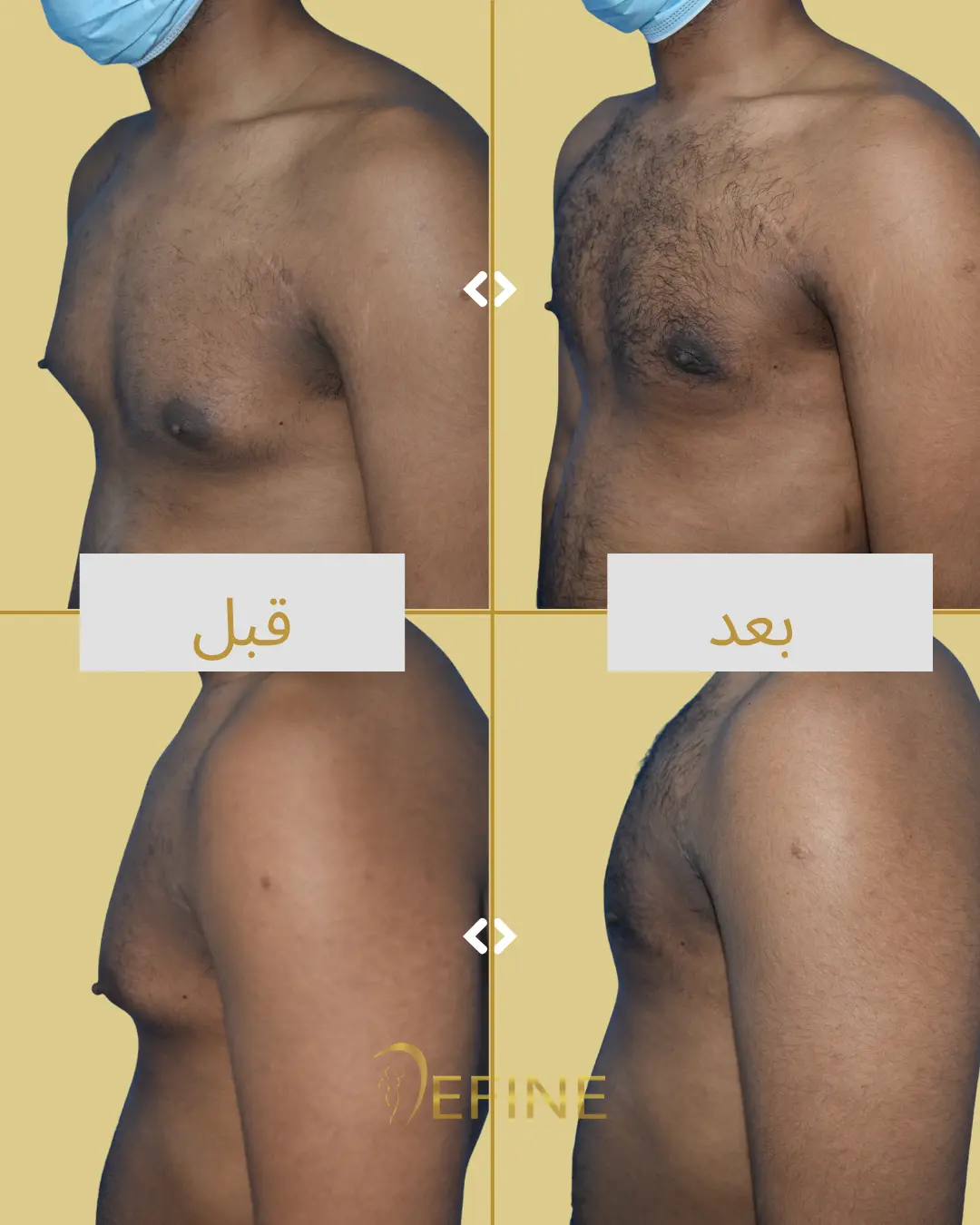
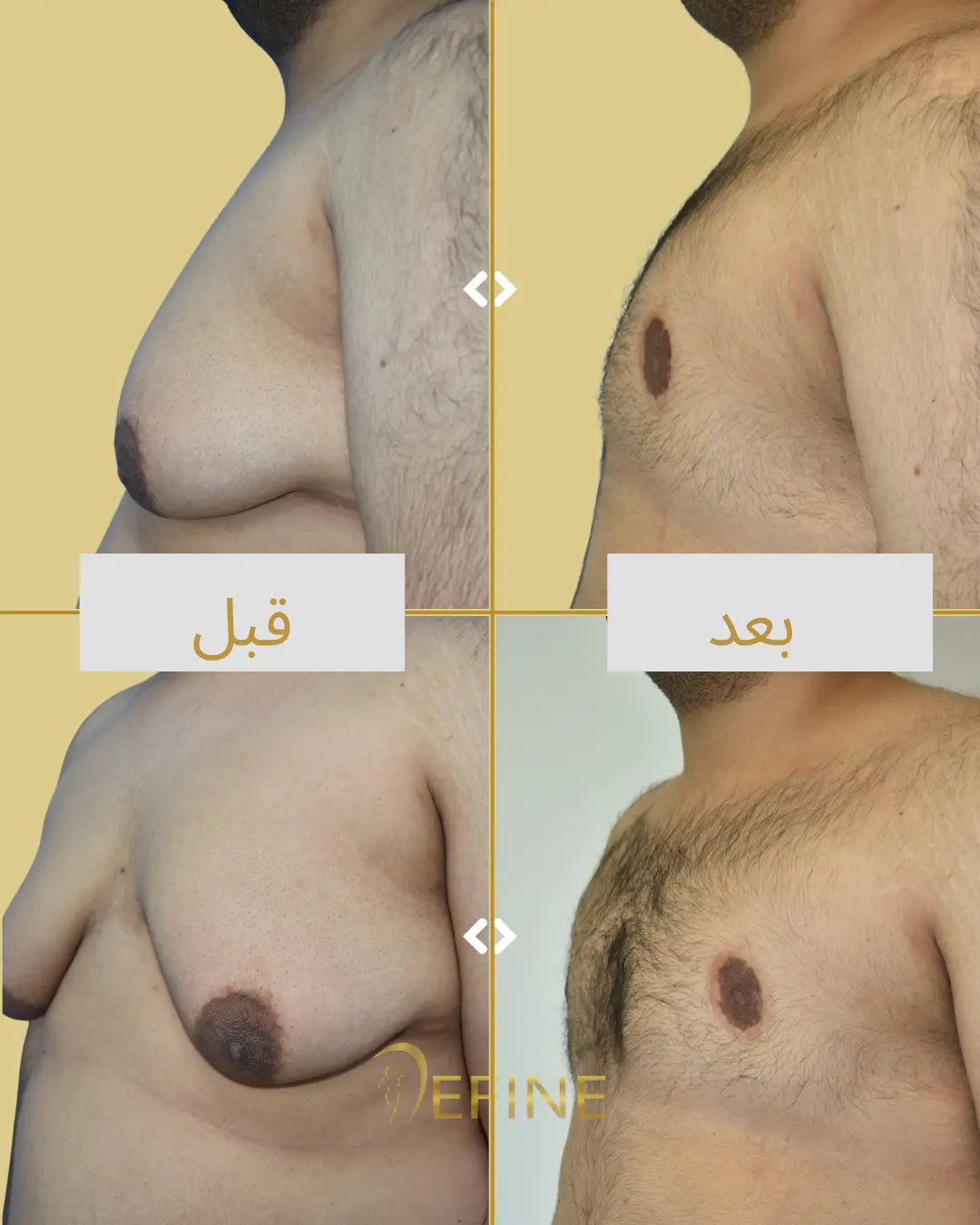
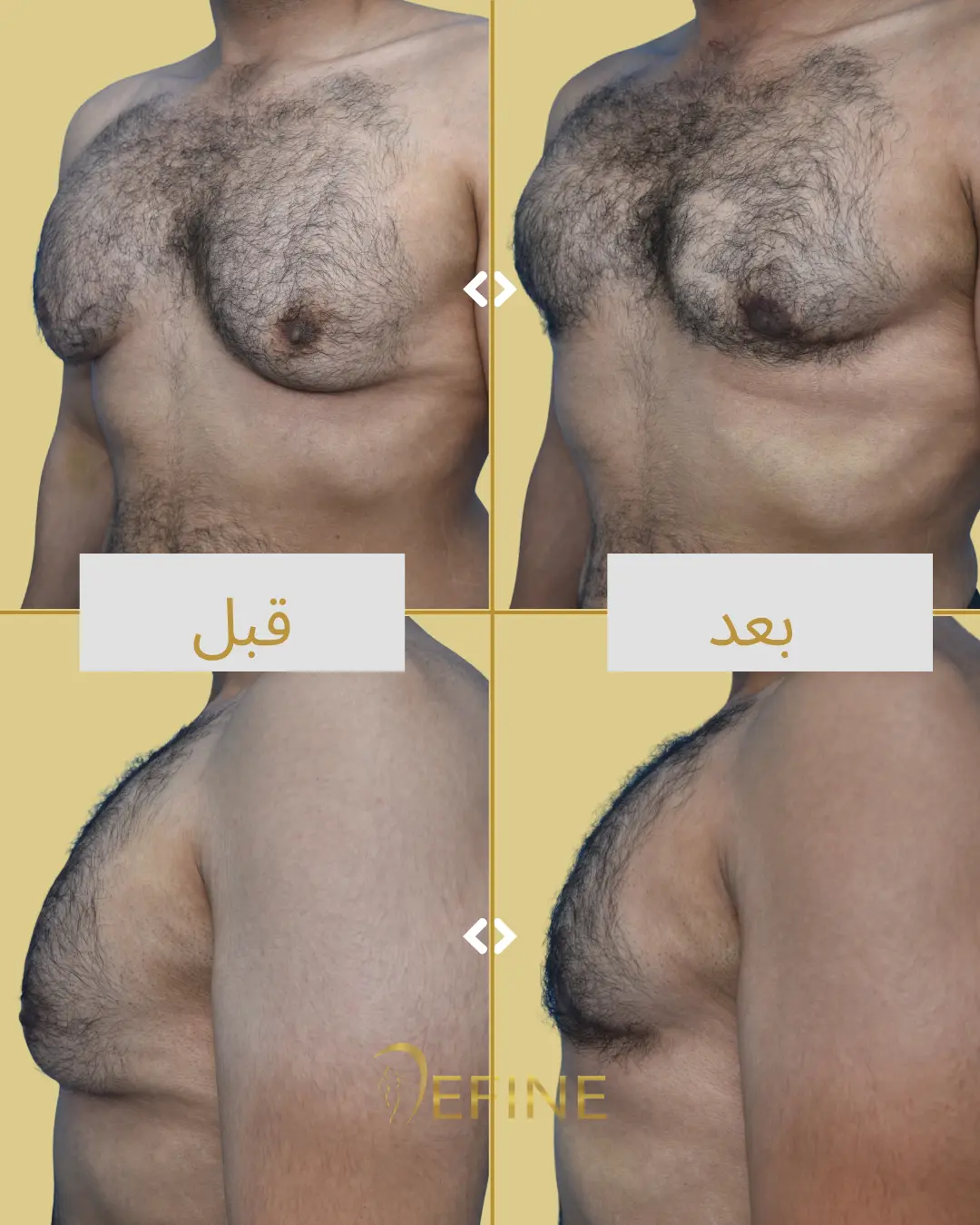
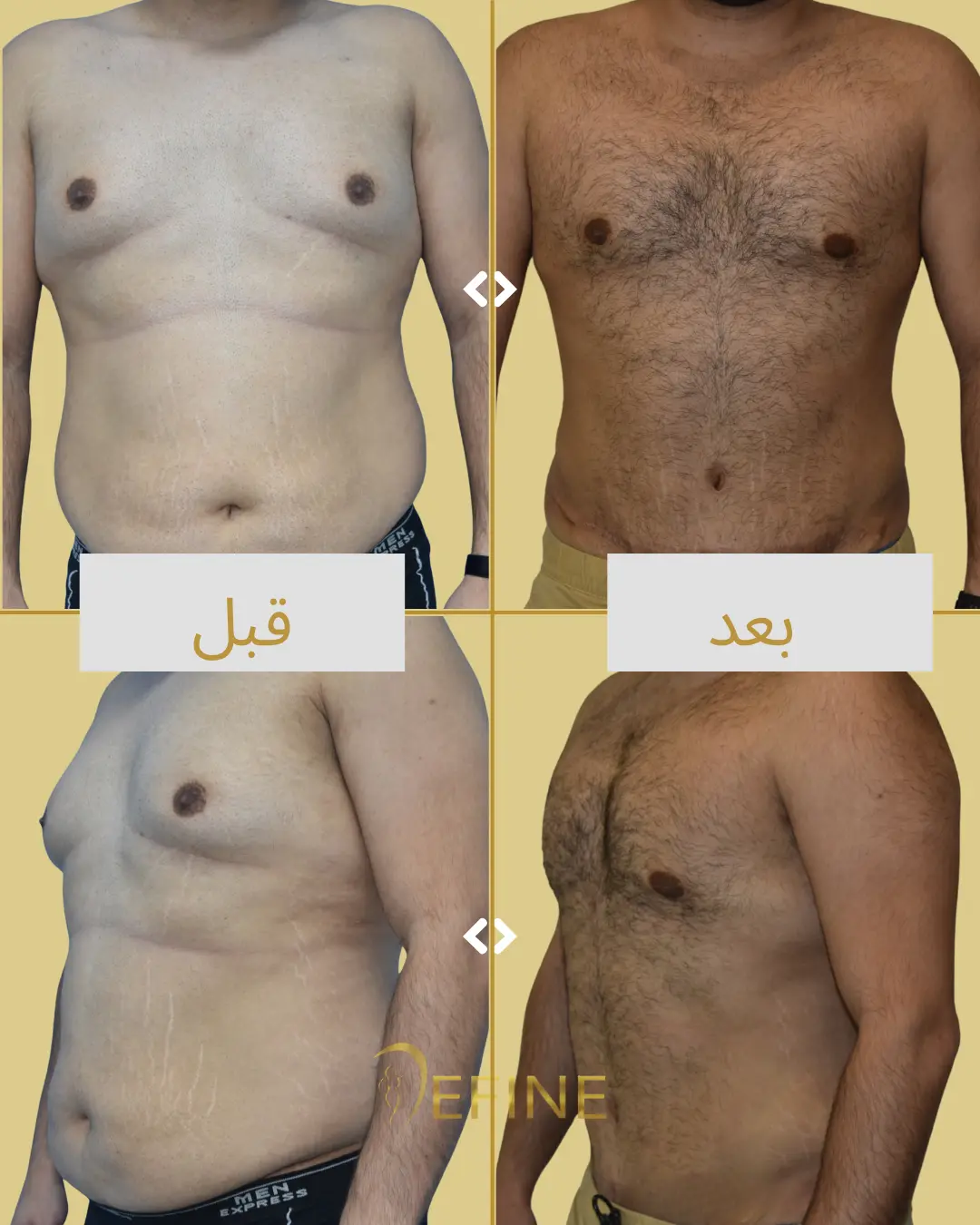
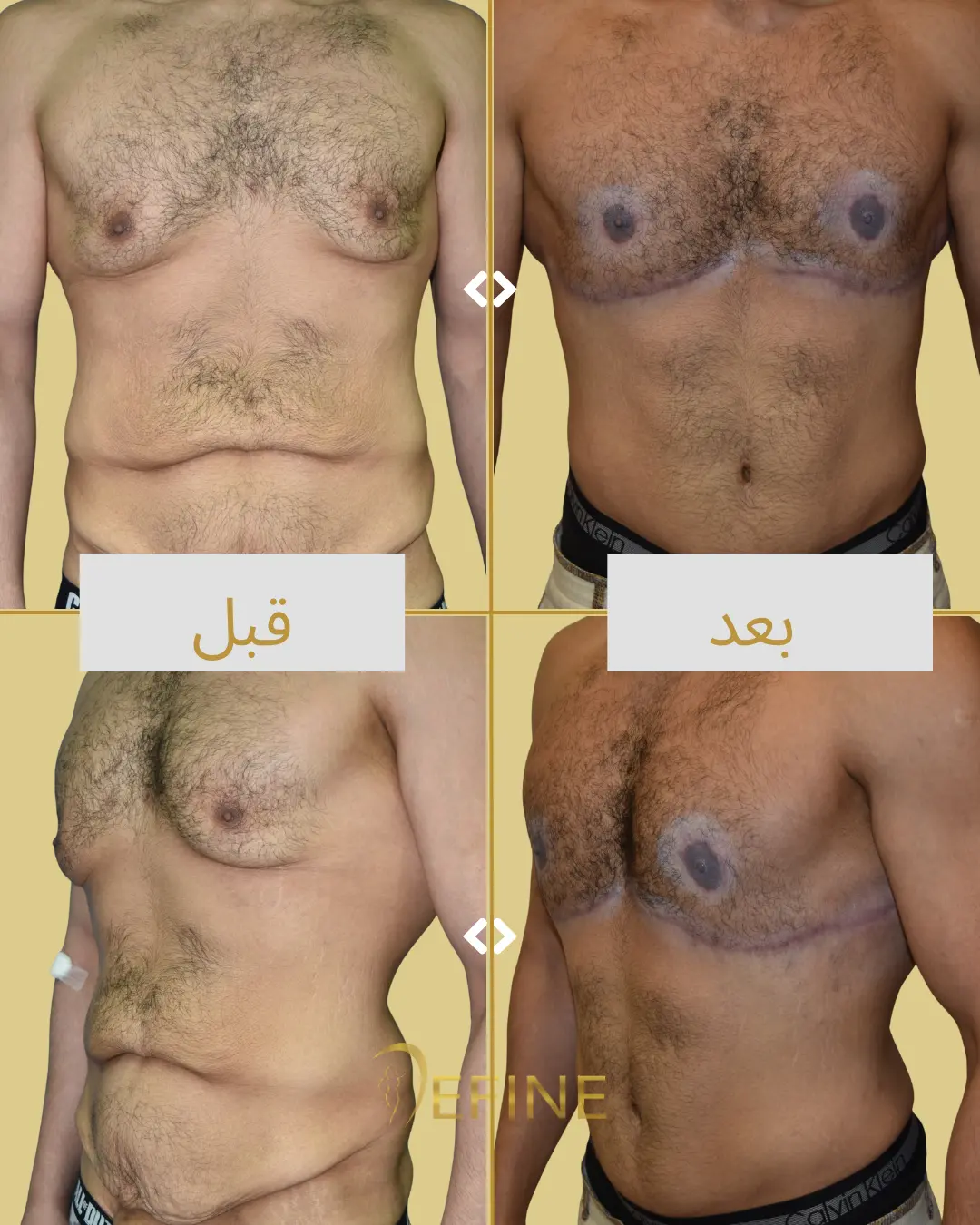
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of male breast tissue, which can lead to the development of feminine-looking breasts. This condition may occur due to hormonal imbalances, obesity, genetics, aging, or the use of certain medications or substances. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts and can cause physical discomfort and emotional distress. Gynecomastia surgery, or male breast reduction, is a cosmetic procedure designed to reduce excess breast tissue and restore a flatter, more masculine chest contour. The procedure can involve liposuction, excision of glandular tissue, or a combination of both.
Frequently Asked Questions about Gynecomastia Surgery:
Good candidates for gynecomastia surgery are men who have enlarged breast tissue that has not responded to diet or exercise, and who are in good overall health.
Gynecomastia is often caused by an imbalance between the hormones estrogen and testosterone. It can occur during puberty, due to aging, or as a result of obesity. Certain medications, substance abuse (like alcohol or steroids), or medical conditions can also contribute to its development.
Most patients can return to work or light activities after 1-2 weeks, while more strenuous activities should be avoided for 4-6 weeks. Full recovery typically takes about 6-8 weeks. Swelling and bruising will gradually subside over the first few weeks.
The incisions are typically made around the areola or in the natural folds of the chest, which helps to minimize visible scarring. Over time, scars tend to fade and flatten, though they may be visible for several months after surgery.
Most patients can return to work or light activities after 1-2 weeks, while more strenuous activities should be avoided for 4-6 weeks. Full recovery typically takes about 6-8 weeks. Swelling and bruising will gradually subside over the first few weeks.